Describe the Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells Using Endosymbiotic Theory Hypothesis
Endosymbiosis is supported particularly by studies of mitochondria and chloroplasts. The endosymbiotic theory states that some of the organelles in todays eukaryotic cells were once prokaryotic microbes.
Fhs Bio Wiki Endosymbiotic Theory
Definition of the Embosymbiotic theory 17-2 427 theory that eukaryotic cells formed from a symbiosis among several different prokaryotic cells.
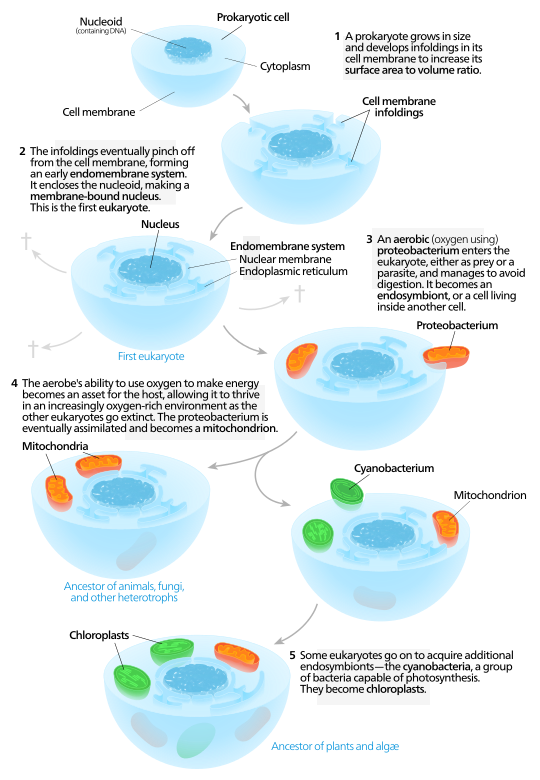
. The hypothesis of endosymbiosis is at present the most widely accepted theory on the evolution of the eukaryotic cell. In addition to making energy the first mitochondria probably helped the cell survive the newer form of the atmosphere that now. As the site of cellular respiration mitochondria.
Some of the small cells were able to break down the large cells wastes for energy. The endosymbiotic theory explains how eukaryotic cells evolved. Endosymbiotic theory stats that the modern eukaryotic cells mitochondria evolved in steps through inter-cooperation into cells from a nuclear line of descendants of chemoorganotrophic and phototrophic symbionts.
Known as the Endosymbiotic Theory Lynn Margulis proposed that the mitochondria or the part of the cell that makes usable energy was once a prokaryote that was engulfed but not digested by the primitive eukaryote. The theory states that chloroplasts developed from. This current theory states that the mitochondria and chloroplasts contained within the eukaryotic cell are there due to the integration of free living bacteria which implement aerobic metabolism chemoorganotrophic bacteria and bacteria which implement oxygenic.
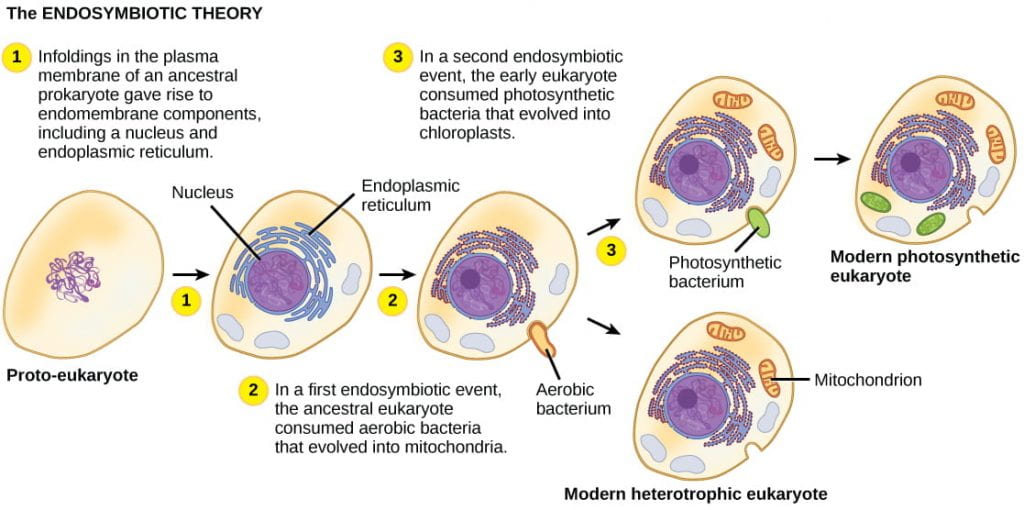
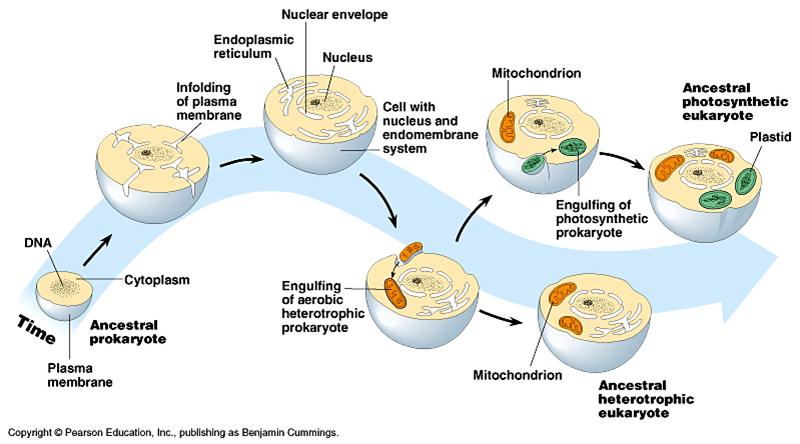
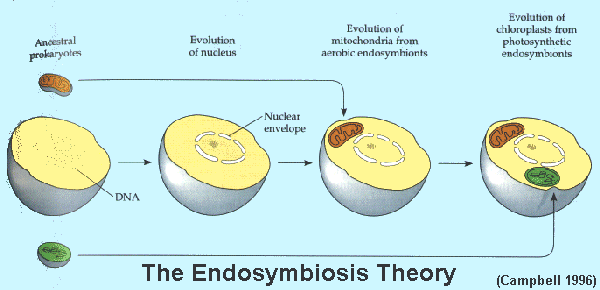
In accordance with the endosymbiotic theory of origin of eukaryotic cells the eukaryotes have evolved from number of cells that happened to join together and form a single eukaryotic cell. Then later a similar event brought chloroplasts into some eukaryotic cells creating the lineage that led to plants. Over millions of years of evolution mitochondria and chloroplasts have become more specialized and today they cannot live.
They began to live in what we call symbiotic relationships. Since the symbiotic hypothesis states that mitochondria and chloroplasts arose from bacteria entering a eukaryotic cell to form a symbiotic relationship similarities between bacteria and these semiautonomous organelles show strong convincing evidence that this hypothesis is correct Evidence for the Endosymbiotic Hypothesis Steps of evolution of Eukaryotic cells via. The endosymbiotic event that generated mitochondria must have happened early in the history of eukaryotes because all eukaryotes have them.
Endosymbiotic theory is the unified and widely accepted theory of how organelles arose in organisms differing prokaryotic organisms from eukaryotic organisms. The Endosymbiotic hypothesis is one of the oldest evolutionary hypotheses still in use today. When one organism actually lives inside the other its called endosymbiosis.
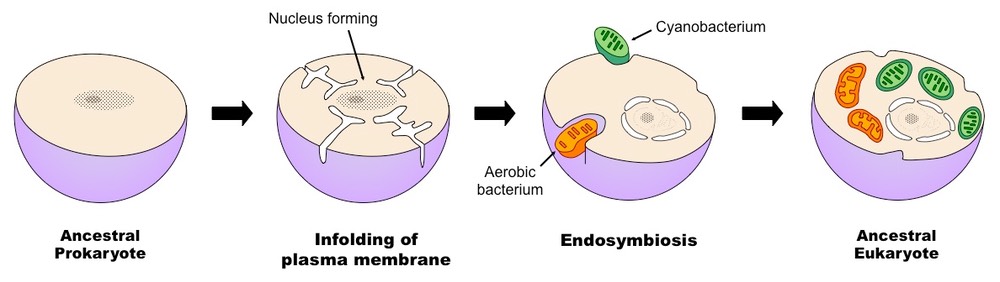
In this theory the first eukaryotic cell was probably an amoeba-like cell that got nutrients by phagocytosis and contained a nucleus that formed when a piece of the cytoplasmic membrane pinched off around the chromosomes. They supplied energy not only to themselves but also to the large cell. The hypothesis is that all eukaryotic cells have evolved from a symbiotic association of prokaryotesendosymbiosis.
Eukaryotic cells may have evolved when multiple cells joined together into one. The main characteristic of the eukaryotic cell Figure 1 is the existence of a nucleus in prokaryotes the genome is only very rarely surrounded by a membrane surrounded by a cytoplasm containing many organelles such as mitochondria Organelles of the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells plants algae animals. Describe the hypothesized steps for the evolution of eukaryotic cells via endosymbiosis.
Smaller prokaryotic cells were immersed by or attacked larger prokaryotic cells. This type of symbiosis entails a bigger cell acting as the host and a smaller cell acting as the endosymbiont. In endosymbiotic theory consistent with general evolutionary theory all.
An endosymbiont is one organism that lives inside of another one. Using our reading this week and with the understanding from my readings the first eukaryotic cells evolved from an interdependent relationship between two or more prokaryotic cells. The theory of endosymbiosis states that eukaryotic cells evolved when some prokaryotes were engulfed by others and avoided being digested.
The theory that explains how this could have happened is called endosymbiotic theory. Evidence to support the endosymbiotic theory 17-2 428-429. The endosymbiotic theory of the origin of eukaryotic cells states that all the individuals are evolved from the same individual.
Margulis spent much of the rest of the 1960s honing her argument that symbiosis see figure below was an unrecognized but major force in the evolution of cells. It is thought that mitochondria and chloroplasts View the full answer. The bigger cell absorbed or took in the smaller one according to the.
Recent evidences justify that organelles have originated from the endosymbiotic association of ingested aerobic and photosynthetic prokaryotes the precursors of mitochondria and chloroplast respectively. The large and small cells formed a symbiotic relationship in which both cells benefited. The origin of eukaryotic cells was largely a mystery until a revolutionary hypothesis was comprehensively examined in the 1960s by Lynn Margulis.
The more well documented and generally accepted theory for the origin of eukaryotic organelles is endosymbiotic theory. The evolution of aerobic prokaryotes was an important step toward the evolution of the first eukaryote but several other distinguishing features had to evolve as well. After all thats just what youd expect from a symbiotic partner.
It is assumed that the early living forms formed an endosymbiotic relationship. What hypothesis explains the origin of eukaryotic cells17-2 427 The endosymbiotic theory. In 1970 she published her argument in The Origin of Eukaryotic Cells.
The endosymbiotic theory describes how a large host cell and ingested bacteria could easily become dependent on one another for survival resulting in a permanent relationship.
Eukaryotes And Their Origins Organismal Biology
Endosymbiosis Evidence Evolution Schoolworkhelper

Endosymbiosis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Eukaryotic Origins Boundless Biology

The Endosymbiotic Theory Of The Origin Of Mitochondria And Download Scientific Diagram

7 8 The Endosymbiotic Theory Biology Libretexts

Endosymbiotic Theory Eq How Were Eukaryotic Cells Originally Formed Ppt Download

8 16d Endosymbiotic Theory And The Evolution Of Eukaryotes Biology Libretexts

23 1c Endosymbiosis And The Evolution Of Eukaryotes Biology Libretexts

Possible Evolutionary Scenario For The Origin Of Eukaryotic Cells And Download Scientific Diagram

This Figure Illustrates The Endosymbiotic Origin Of Mitochondria And Download Scientific Diagram
Endosymbiotic Theory Of The Origin Of Eukaryotic Cells

Endosymbiotic Theory Risser Microbiology F2017 Openstax Cnx

8 16d Endosymbiotic Theory And The Evolution Of Eukaryotes Biology Libretexts
The Theory Of Endosymbiosis And Its Implications In The Evolution Of The Three Domains By Michael Kwon Medium

Comments
Post a Comment